Barker and Black Slug Test Solution for Fractured Aquifers
Related Solution Methods
Additional Topics
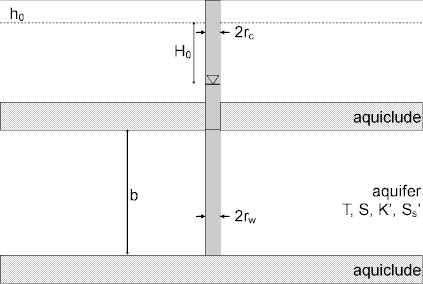
A mathematical solution by Barker and Black (1983) is useful for determining the hydraulic properties (transmissivity and storage coefficient of the fractures; hydraulic conductivity and specific storage of the matrix) of double-porosity fractured aquifers. Analysis involves matching a type curve solution to water-level displacement data collected during a slug test.
AQTESOLV provides visual and automatic methods for matching the Barker and Black solution to slug test data. This easy-to-use and intuitive software promotes rapid and accurate determination of aquifer properties.
Assumptions
The following assumptions apply to the use of the Barker and Black solution:
- aquifer has infinite areal extent
- aquifer is homogeneous, isotropic and of uniform thickness
- aquifer potentiometric surface is initially horizontal
- control well is fully penetrating
- a volume of water, V, is injected or discharged instantaneously from the control well
- flow to control well is horizontal
- aquifer is fractured with double porosity and slab blocks
- flow is unsteady
- water is released instantaneously from storage with decline of hydraulic head
References
Barker, J.A. and J.H. Black, 1983. Slug tests in fissured aquifers, Water Resources Research, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 1558-1564.