Analysis of a Constant-Rate Pumping Test in a Confined Aquifer
If you have AQTESOLV v4.0 or higher, you should perform an updated version of this tutorial found in the Quick Start chapter of the Help file installed with the software.
Walton (1962) presented data for an eight-hour, constant-rate pumping test in a nonleaky confined aquifer conducted July 2, 1953 at Gridley, Illinois. The discharge rate maintained in Well 3 was 200 gallons-per-minute (gpm). Drawdown was monitored in Well 1 located 824 ft from the pumped well. The reported thickness of the sand and gravel aquifer is 18 feet.
Start the AQTESOLV application (v. 3.0 or higher) and follow the steps below.
- Choose File>New and select Pumping Test Wizard from the list to create a new data set for a pumping test. Click OK to proceed with the Pumping Test Wizard.
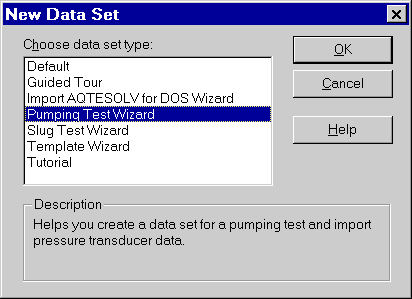
- Enter units of measurement as shown and click Next.
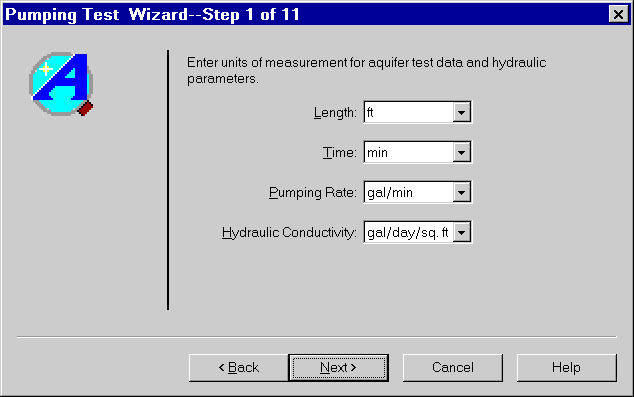
- Enter project information as shown and click Next.
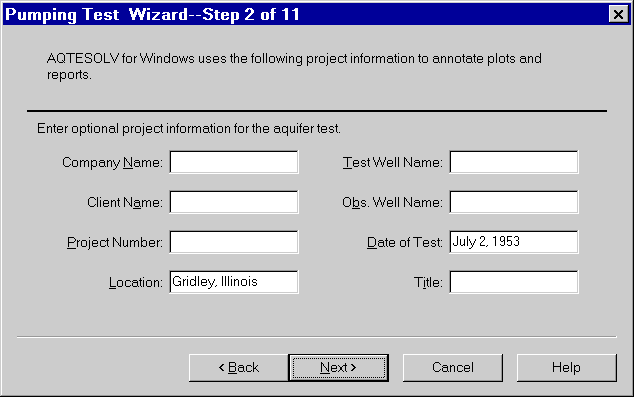
- Enter aquifer data as shown and click Next.
- Click Next twice to skip the steps for fractured aquifer data.
- Enter pumping well information as shown. The default X and Y coordinates place the pumping well at the center of the coordinate system. Click Next.
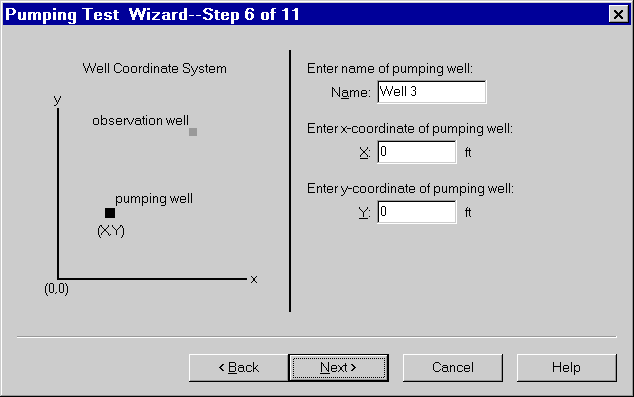
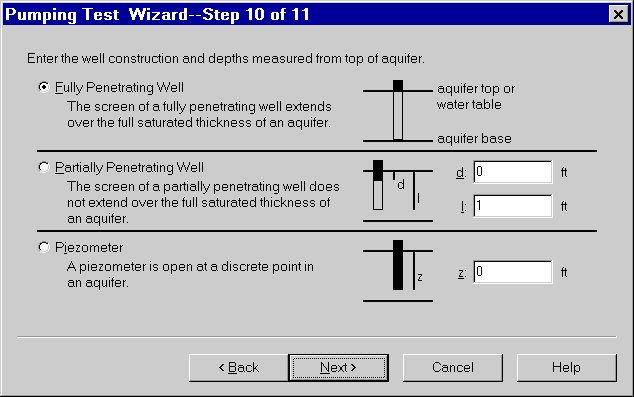
- Choose the option for a Fully Penetrating Well as shown and click Next.
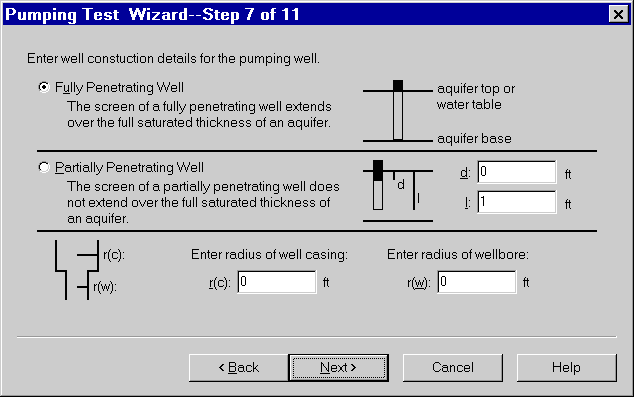
- Enter pumping rate data in the spreadsheet as shown. Click Next.
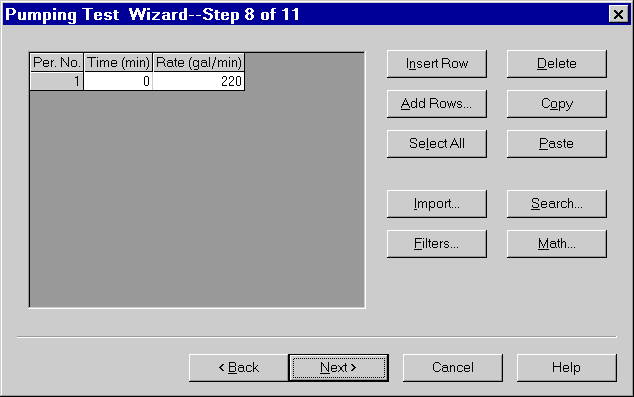
- Enter observation well data as shown and click Next.
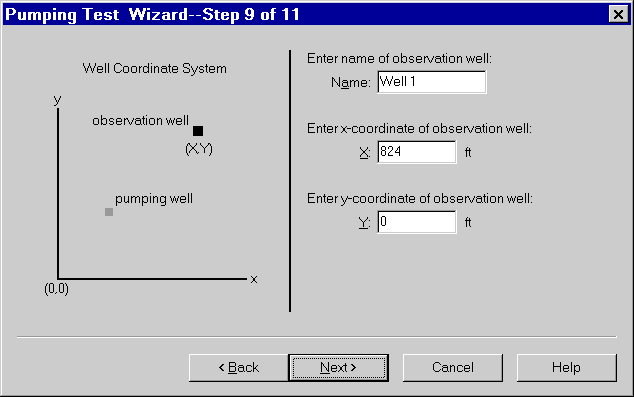
- Choose the option for a Fully Penetrating Well as shown and click Next.
- Enter the following time and displacement measurements into the spreadsheet for observation data. You can copy the data shown below and paste it into AQTESOLV for Windows using the Windows clipboard.
3 0.3
5 0.7
8 1.3
12 2.1
20 3.2
24 3.6
30 4.1
38 4.7
47 5.1
50 5.3
60 5.7
70 6.1
80 6.3
90 6.7
100 7
130 7.5
160 8.3
200 8.5
260 9.2
320 9.7
380 10.2
500 10.9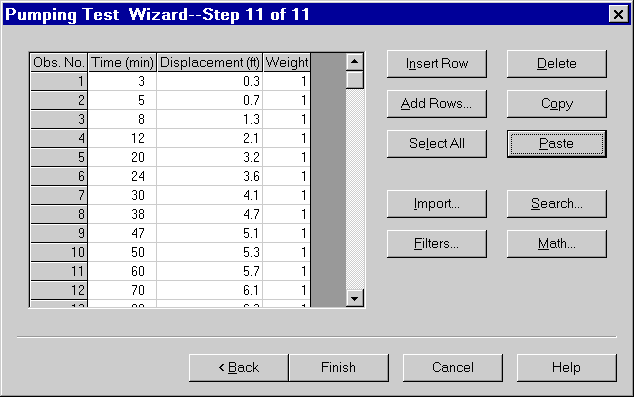
- Click Finish to complete the Pumping Test Wizard.
- If you entered all of the data into the Pumping Test Wizard correctly, the Error Log displayed on the screen should show no errors in the data set. If the Error Log identifies any mistakes, you can correct them by choosing options from the Edit menu.
- Choose File>Save As to save your work. Choose a folder and enter Gridley Well No. 1 for the name of the file. AQTESOLV for Windows saves the data set with an .aqt extension.
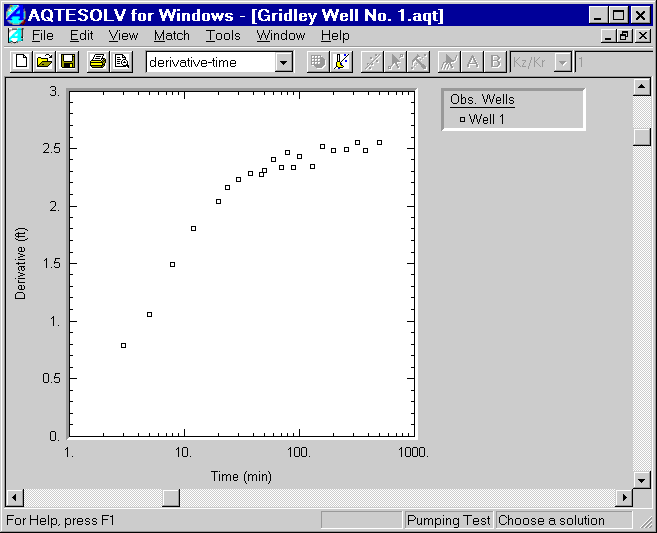
- Choose View>Derivative-Time to view a derivative plot of the data. Smooth the derivative data by choosing View | Options and clicking the Derivative tab. Select the option for Smoothing and enter a factor of 2. Click OK. The form of the derivative plot for this data set is indicative of radial flow in a confined aquifer.
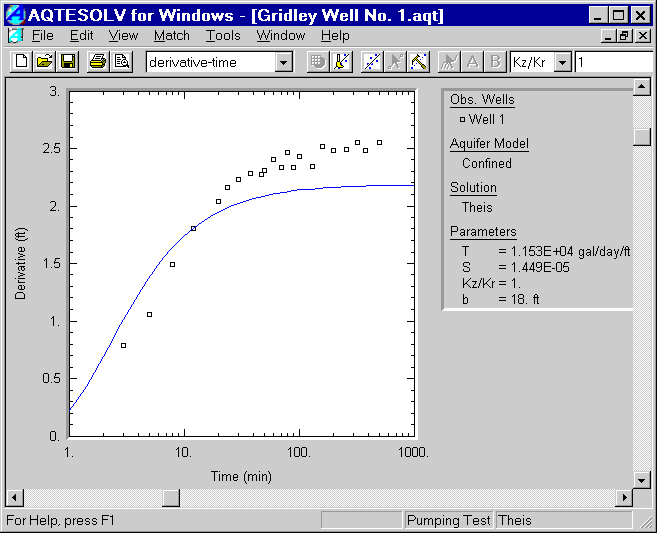
- Choose Match>Solution and select Confined - Theis (1935) from the list. Click OK. AQTESOLV for Windows displays the Theis solution on the derivative plot. Note that prior to estimating the values of T and S for the aquifer, the solution and the data on the derivative plot have the same shape.
- Choose View>Displacement-Time to display the Theis type curve and data. Right click the mouse over the plot and select Log to display the plot with log-log axes.
- Choose Match>Automatic and click Estimate to estimate aquifer properties using automatic estimation. When the estimation procedure has finished, click OK and then Close to close the summary window. Click OK to view the new position of the type curve with the estimated values of T and S.
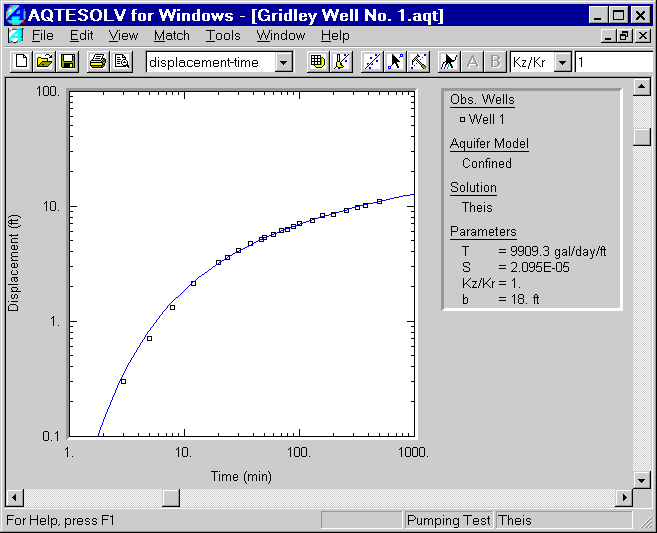
- Choose Match>Visual if you would like to fit the curve using visual matching. Move the mouse over the plot. Click and hold the left mouse button down to drag the type curve to a new location.