McElwee and Zenner Slug Test Solution for Confined Aquifers
Related Solution Methods
Additional Topics
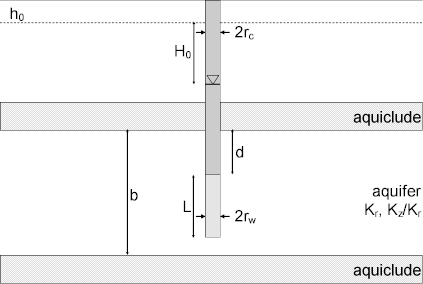
A mathematical solution by McElwee and Zenner (1998) is useful for determining the hydraulic conductivity of nonleaky confined aquifers. The solution accounts for inertial effects in the well and oscillatory response. Analysis involves matching a type curve to water-level displacement data collected during a slug test.
AQTESOLV provides visual and automatic methods for matching the McElwee and Zenner solution to slug test data. This easy-to-use and intuitive software promotes rapid and accurate determination of aquifer properties.
Assumptions
The following assumptions apply to the use of the McElwee and Zenner slug test solution:
- aquifer has infinite areal extent
- aquifer is homogeneous and of uniform thickness
- aquifer potentiometric surface is initially horizontal
- control well is partially penetrating
- a volume of water, V, is injected or discharged instantaneously from the control well
- aquifer is nonleaky confined
- flow is quasi-steady-state
Solution
Options
AQTESOLV provides the following options for the McElwee and Zenner slug test solution:
- partially penetrating wells
- hydraulic conductivity anisotropy
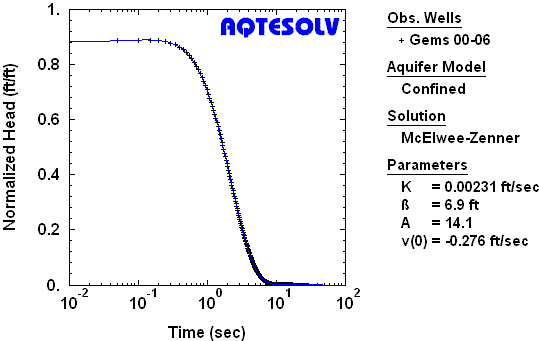
Benchmark
References
McElwee, C.D. and M. Zenner, 1998. A nonlinear model for analysis of slug-test data, Water Resources Research, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 55-66.
McElwee, C.D., 2000. Implementation of a nonlinear model for analysis of slug tests, Kansas Geological Survey Computer Program Series 2000-01, Lawrence, Kansas.